
Like epigenetics and exosomes, neurocosmetics represent a revolutionary approach for skin care incorporating neuroscience principles, leveraging the skin-brain connection to improve skin health and beauty. The term itself is a fusion of the words neuroscience and cosmetics. It differs from psychodermatology which like neurocosmetics connects the interaction between mind and skin, but in a different way. Some describe it as how simple sensory stimulation can improve our overall wellbeing and call it "mood beauty", however this doesn't do it justice as neurocosmetics go beyond mood boosting skincare.
DEFINITION NEUROCOSMETICS Dermatologist Professor Laurent Misery back in 2002 described that neurocosmetics are products which are supposed to modulate the neuro-immuno-cutaneous-system (NICS) function at an epidermal level. Skin cells can produce neuromediators, which are mediators for transmission of information between skin, immune and the nervous system. All skin cells express specific receptors for neuromediators and by binding of the neuromediator to its receptor, modulation of cell properties and skin functions are induced like cell differentiation and proliferation (renewal), pigmentation, etc. Hence, keratinocytes, Langerhans cells, melanocytes, endothelial cells, fibroblasts and the other cells of the skin are modulated and controlled by the nerves and in return skin is able to modulate neuronal activity and growth. [1] SKIN-BRAIN CONNECTION In an article from the International Journal of Novel Research and Developments, the skin-brain connection was described as a psychobiological concept that highlights how emotions, stress, and neurotransmitters impact skin health. Indicating that the skin acts as a neuroimmunoendocrine organ, emphasizing its sensitivity to neural signals and stress responses. [4] CUTANEOUS NERVOUS SYSTEM The skin a sophisticated sensory organ that allows you to interact with your environment through touch and feel. It contains a complex network of nerves that send information about sensations like pressure, pain, itch and temperature from the skin through the spinal cord to the brain [9]. The dynamic interactions between the skin and the nervous system is influenced by factors like stress and inflammation, which can impact skin health and ageing. [7] Nerves in the skin: These nerves are like tiny messengers that tell your brain about what your skin is feeling: pressure, heat or pain. Types of nerve fibers: Some are thick and wrapped in a protective coating, which helps them send messages quickly. Others are thin and slow but are very good at sending messages about pain or temperature changes. [3] Sensory receptors: These receptors can tell if something is touching the skin lightly or if there's a lot of pressure. They can also sense if something is hot, cold, or causing pain. [3] Autonomic nervous system: Part of the cutaneous nervous system helps control things that happen in the skin automatically, like sweating to regulate body temperature. [8] Nerve cells: There are about 20 different types of neurons in our skin. [10] The contribution of epidermal keratinocytes to NICS [3]
CUTANEOUS NEURO-AGEING Neuro-ageing is defined as the changes in the nervous system which cause continuous neurodegeneration due to oxidative stress, neuroinflammation or impaired neuromodulation. As skin ages, Aβ-toxin (increased by oxidative stress) accumulates at the nerve endings innervating the tissue, causing disrupted cellular communication, particularly affecting fibroblasts’ ability to produce collagen and extracellular matrix. On top there is a decrease of nerve growth factor (NGF) production, important for the development and maintenance of nerve cells. Different factors can lead to a drop in NGF production, resulting in malfunctioning keratinocytes and reduced lipolytic activity of adipocytes, visibly impacting skin hydration and firmness. [6] Skin nerve fibres are significantly reduced in number following UV irradiation and in ageing skin [5] and therefore neuro-protectors or targetting neurodegeneration can reduce stress manifestations and promote healthy cellular communication for optimal skin function. [3] Although not much is known regarding skin specific or topical neuroprotectors (most research was focussed on the brain), probably potent anti-oxidants, by significantly reducing oxidative stress from UV and blue light and anti-inflammatory ingredients may inhibit skin neuro-ageing and can be neuroprotective especially when combined with sunscreen and strengthening of the skin barrier. NEUROCOSMETIC VARIETY OF ACTIONS
THE FUTURE OF NEUROCOSMETICS The neurocosmetics market is booming, with a projected value of USD 2.69 billion by 2030. [11] The future of neurocosmetics holds promise for innovative ingredients and concepts that harness new neuroscientific insights to revolutionize skin care and sunscreen formulations, to cater to both physical and emotional aspects of skin health and beauty. Take care! Anne-Marie References
Comments

If you've scrolled through Instagram, you may have caught a glimpse of dermatologists raving about LED masks emitting red light, the secret, evidenced based weapon behind skin rejuvenation known as photo biomodulation. It uses low-powered light within the red to near-infrared range (wavelengths from 632 to 1064 nm) to induce a biological reaction aka stimulate cellular processes. The wonders of red light, also known as LLLT (low-level laser therapy), PBM (red light photo-biomodulation), or PBMT (photo-biomodulating therapy), extend far beyond non-invasive skin rejuvenation. I am not a fan of devices for home use, mostly because of lacking safety and/or efficacy, PBM definitely earned it's prominent spot in my skincare routine.
A summary of the benefts of red light with and without near infrared light for skin Numerous studies have demonstrated the effectiveness of red and infrared light therapy for skin rejuvenation. A combination of red light and near IR light has proven to stimulate the production of collagen (I & III) plus elastin production (Li WH et al Int J Cosmet Sci 2021), enhance mitochondrial ATP production, cell signaling, growth factor synthesis, rebalance ROS (reactive oxidative species) and reduce inflammation. Stem cells can be activated allowing tissue repair and healing. Wrinkle and scar reduction was observed and it can reduce UV damage both as treatment and prophylactic measure. In pigmentary disorders such as vitiligo, it can increase pigmentation by melanocyte proliferation and reduce depigmentation by inhibiting autoimmunity (Pinar Avci et al. Semin Cutan Med Surg. 2013 & Mitchell J Winkie et al. Review Photodermatol Photoimmunol Photomed A focused review of visible light therapies for vitiligo 2024). It has the potential to activate both keratinocytes (epidermis) and fibroblasts (epidermal junction and dermis). With consistent use, you can expect a reduction of lines and wrinkles, improvement of skin tone and texture. PBMT (when done effective and safe) will compliment both your skin rejuvenating and regenerating at home skincare regimen and in-office procedures or even post-surgical skin recovery. ATP ATP (adenosine triphosphate) is the primary source of energy for cellular processes and plays a crucial role in various biological functions. When red light with specific wavelengths (630 nm to 638 nm and 810 nm) is absorbed by the skin cells, it stimulates the mitochondria, which are the powerhouses of the cells responsible for ATP synthesis. This increase in ATP production is providing cells with more energy to carry out their functions effectively and has several beneficial effects on the skin like boosting cellular metabolism, promoting more efficient nutrient uptake and waste removal. The increased ATP levels facilitate collagen synthesis by fibroblasts, a vital component for skin structure, elasticity and firmness and reduction of lines and wrinkles.. ATP aids in the repair and regeneration of damaged skin cells. It accelerates the healing process, making it beneficial for wound healing, post-surgical recovery, and addressing skin issues such as acne scars. ROS (Reactive Oxidative Species) By modulating ROS levels, red light therapy helps reduce oxidative stress and its detrimental effects on the skin. ROS are highly reactive molecules that are naturally produced by cells as byproducts of metabolic processes. While low levels of ROS play important roles in cellular signaling and immune responses, excessive ROS can lead to oxidative stress and damage to cells and tissues. Restoring the balance of ROS result in improved skin health, reduced inflammation, and enhanced skin rejuvenation. Red light therapy has been shown to modulate reactive oxidative species (ROS) levels in the skin by promoting antioxidant defense mechanisms and reducing oxidative stress:
The difference between LLLT and PBM LLLT refers specifically to the use of lasers, which produce coherent, focussed and an intense beam of monochromatic light, while PBM has a broader range of light sources, may include laser as well as light-emitting diodes (LEDs) and other non-laser devices. LEDs are often used in PBM because they are cost effective, versatile and have the ability to cover large treatment areas. LLT uses higher power densities with more energy and has a shorter treatment duration in comparison to PBM to achieve desired therapeutic effects. While there are similarities in terms of mode of action", there is a difference of light source, treatment application and parameters. Based on consensus, PBM and PBMT are considered the correct way to describe this photonic specialty for therapeutic applications. In this post I will focus on PBM and specifically LEDs. LED masks and LED panels LED masks specifically produced by the brand Omnilux (FDA cleared) are currently very popular for very good reasons; they are safe and effective when the LEDs emit the right wavelengths and used in the recommended frequency. Omnilux combines 2 therapeutically effective and complimentary wavelengths: 633nm and near-infrared 830 nm. Both wavelengths (more precise 630nm + 850nm) I would recommend to minimally look for in any red LED device, which will disqualify most LED masks and panels in the market! I've include some (not affiliated) links to devices below. Both masks and panels can be effective, however most panels are stronger in comparison to masks 60 mW/cm² vs mW/cm²), hence have the benefit of a shorter treatment time to get a similar result. Intensity and power of red light therapy devices are typically measured in terms of irradiance (measured in milliwatts per square centimeter, mW/cm²) and radiant flux (measured in watts, W), which quantify the amount of light energy emitted by the device. Wearing a mask during a hot summer or in a warmer climate will make you sweat and depending on the materials of the mask and straps, they may be very uncomfortable to wear. Panels have the benefit that they give a more even distribution of emitted light as masks are worn on the face and thus the LED bulbs are pushed on a small skin surface area, panels can cover a larger area (depending on their size) and are more versatile in use, as area's like neck, décolletage, or knees are easier to treat with a panel. With a mask you may be more mobile, although I would not recommend walking around while using the mask. My personal preference would be a panel for the reasons mentioned before and panels are more suitable (more hygienic) for family sharing. My son can use it after an intense workout to speed up his recovery and I like to use it for purposes beyond photo-biomodulation or skin rejuvenation, for example to improve my sleep. With a panel I get more "bang for my buck". 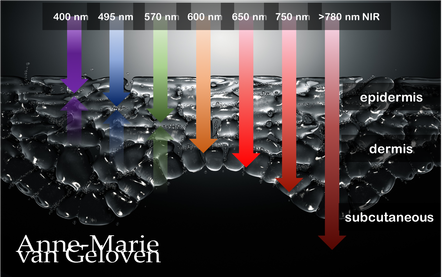
Red light and NIR (Near Infra Red light) have the ability to penetrate varying depths of the skin, resulting in distinct benefits, thus combinations of wavelengths will provide complementary effects.
630 nm Wavelength This wavelength is often used for its skin rejuvenation benefits. It has a relatively shallow penetration depth and is absorbed closer to the surface of the skin primarily affecting the epidermis. 630nm light is associated with increased circulation, reduce inflammation, improved skin tone & texture, aiding in the delivery of nutrients and oxygen to skin cells, and stimulating the production of collagen, leading to improved skin elasticity and a reduction of the appearance of fine lines & wrinkles. 660 nm Wavelength At 660nm, red light can penetrate a little deeper into the skin, reaching the dermis. It is known for its ability to stimulate collagen production, enhance cellular metabolism, and promote anti-inflammatory effects, helping to reduce redness and inflammageing. It also promotes wound healing, making it beneficial for post-surgical or post-trauma skin recovery. 810 nm Wavelength Improve healing & recovery & accelerate wound healing. 830 nm Wavelength Accelerate healing, reduce infection, improve aesthetic outcome following plastic surgery, increase endorfines (mood-enhancing), improve bone repair and growth. 850 nm Wavelength Improve general inflammation body, enhance muscle recovery, improve wound healing, reduced fine lines, wrinkles and hyperpigmentation. Always consult a qualified healthcare professional or dermatologist to determine if and what the most suitable red light therapy approach is for your particular skin condition and rejuvenation goals. Take care! References: Hamblin, Michael R. "Mechanisms and applications of the anti-inflammatory effects of photobiomodulation." AIMS biophysics 4.3 (2017): 337-361. Barolet, Daniel. Regulation of Skin Collagen Metabolism In Vitro Using a Pulsed 660 nm LED Light Source: Clinical Correlation with a Single-Blinded August 2009Journal of Investigative Dermatology 129(12):2751-9 Wunsch A, Matuschka K. (2014). A controlled trial to determine the efficacy of red and near-infrared light treatment in patient satisfaction, reduction of fine lines, wrinkles, skin roughness, and intradermal collagen density increase. Journal of Cosmetic and Laser Therapy, 16(5), 232-237. Avci P, et al. (2013). Low-level laser (light) therapy (LLLT) in skin: stimulating, healing, restoring. Seminars in Cutaneous Medicine and Surgery, 32(1), 41-52. Links to some devices which combine 630 nm and 850 nm: FDA-approved devices ensure safety and regulatory compliance, however the panels are more powerful: Omnilux(tm) Mask (FDA clearance) Very affordable panel (no FDA clearance) Affordable panel (no FDA clearance) 
Skin ageing is a biological degenerative process, marked by loss. The number of patients seeking nonsurgical rejuvenation of the face and the body is continuing to increase due to a growing ageing population concerned with physical appearance. Women wish to maintain a youthful appearance and attractiveness represent 92% of all cosmetic procedures.(1) Men are keen to maintain physical characteristics associated with virility.(2) Millennials are also increasingly concerned with preserving their beauty and youth.(3) Among the various treatment approaches, different minimally invasive techniques have been developed and dermal fillers currently come second after botulinum toxin type A (BTA).(3) Their use is increasing worldwide.
"The fear of looking done is the number 1 reason why patients don't seek treatment"* The range of fillers available for soft-tissue augmentation is constantly expanding. The latest advances in filler technology include bio-stimulators that exert their aesthetic effect by promoting predominantly collagenesis or biological stimulation of new collagen and sometimes also elastin production. Therewith they provide a biological answer to the skin ageing degeneration process, with gradual and often very natural results. Over the course of last years the knowledge on injectable bio-stimulators has grown, and therewith their safety and popularity as they provide subtle longer lasting results. Facial fillers can be broken into 3 main groups:
Bio-stimulating fillers promote the body’s natural production of some ECM components (mostly collagen) over a period of several months. Their differences are characterized by their property of inducing natural collagen production. SYNTHETIC BIOSTIMULATORS
Calcium Hydroxylapatite Calcium hydroxylapatite: Calcium hydroxylapatite is a type of mineral that is commonly found in human teeth and bones and in injectbales the calcium hydroxylapatite particles are suspended in a gel-like solution. The effects of this material last approximately 18 months with minimal inflammatory response. Radiesse is a biodegradable filler consisting of 30% synthetic CaHA microspheres (diameter of 25-45μm) suspended in a 70% aqueous carboxymethylcellulose gel carrier. The soluble carrier gel evenly distributes the Radiesse CaHA microspheres providing 1:1 correction and gradually dissipates leaving the microspheres at the injection site where they induce collagenesis (collagen type I and mostly collagen type III) by fibroblast activation. Animal studies have shown that this new collagen growth occurs as early as four weeks post-injection and continues for at least 12 months with an average duration of effect of 12 to 18 months, though some results have been noted 24 months post-injection. Radiesse provides both immediate (replacement volume) and long-lasting (collagen biostimulation) volume enhancement. (5) Poly-L-lactic acid PLLA is a biodegradable, bioresorbable biocompatible man-made polymer. This material has wide uses in absorbable stitches and bone screws. The effects of PLLA generally become increasingly apparent over time (over a period of several weeks) and its effects may last up to 2 years. There is an inflammatory response. PLLA is an alpha hydroxy acid polymer of the lactic acid L-enantiomeric structure that has been safely used in many applications and in medicine for more than 30 years. Its use has expanded worldwide, associated with good long-term aesthetic results thanks to its biostimulatory-collagen effect. PLLA-based fillers are supplied as a lyophilized powder to be reconstituted with sterile water. The collagen stimulatory properties were evidenced in human in subjects (n=14) who received PLLA injections (3 sessions, spaced 4 weeks apart) at the postauricular level by collagen histochemical determination on biopsies taken at different times. Increase of collagen type-I was shown at 3 and 6 months. This study opened the new class of collagen stimulators. The long duration of action was demonstrated in a first pivotal study comparing PLLA versus collagen (116/117 subjects, respectively); the long-term safety/efficacy was shown up to 25 months. The rationale for several sessions was first documented in a dedicated article; this modality allows the effect through collagen stimulation, a biological process to occur and avoids overcorrection. PLLA fillers are among the most clinically documented products. (6) Polymers, polycaprolactone The PCL-based collagen stimulator is composed of PCL microspheres suspended in a carboxymethyl-cellulose gel carrier providing immediate and sustained volumizing effects when injected; the morphology, the biocompatibility of the PCL microspheres embedded with the collagen fibers produced all contribute to the creation of a unique 3D scaffold for a sustained effect. Its safety has been investigated in clinical studies and vigilance surveys. It presents the advantage of a slower degradation than polylactic acid (PLLA) or polyglycolic acid (PGA), which both belong to the same chemical family. Both the S and M products induced collagen production. In animal, the M product induced collagen type-III and type-I at early stage (measure at 9 months), and later predominantly collagen type-I, that deposits around the PCL microspheres (measure at 21 months). Many fibroblasts were found near the PCL microspheres. Interestingly, new elastin fibers were also formed, and neovascularization with new capillaries observed as well. (7) NATURAL BIOSTIMULATORS 1. Platelet rich plasma 2. Platelet rich fibrin 3. Polynucleotides like Nucleofill or Nucleadyn 4. Exosomes 5. Alginate 6. Tropoelastin (precursor of elastin molecule) 7. Poly-y-glutamic acid Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP): PRP treatments are produced by spinning a small volume of the patient’s own blood through a centrifuge. This separates and concentrates the blood’s components, including platelet-rich plasma and the “buffy coat,” a solution that contains immune cells. The provider combines these two components with a small amount of calcium chloride (which activates and keeps the PRP stable), then injects them into the treatment area. Over a period of months, PRP stimulates the body’s natural collagen production. Platelet-Rich Fibrin (PRF): PRF is produced using a process similar to PRP concentration. The active material is a fibrin matrix rich in platelets, stem cells, and immune cells. Like PRP, PRF treatment stimulates collagen production and is also implicated in tissue regeneration, though there’s less data on the durability of its effects. Because both treatments use material from the patient’s own body, so there’s no risk of rejection or similar complications. PRF and PRP effects are durable — typically lasting longer than 18 months. Polynucleotides: Polynucleotides are most often natural, highly purified DNA molecules extracted for example from trout gonads and activate specialised cells called myofibroblasts and adipocytes. PN containing devices act as short time temporary fillers thanks to the viscoelasticity of the long DNA fragments and improve skin well‐being (cell growth) and steady self‐repair (tissue regeneration). Read more Exosomes: The use of exosomes at the Aesthetic & Anti-Aging Medicine World Congress in Monaco was discussed during many session and some excellent results were presented. However their use is not yet approved and safety and long-term effect not yet established and largely depends on the source. Read more BOTULINUM TOXIN There is evidence that the neuromodulator or musclerelaxer Botinumtoxin after injection upregulated the expression of type I collagen, decreases the production of some MMPs in fibroblasts, preventing collagen degradation and improves collagen organisation. (8.9.) ENERGY BASED DEVICES Intense Pulsed Light/BroadBand Light, Radiofrequency Microneedling, lasers, High-Frequency Ultrasound, Electromagnetic Tec. stimulate collagen production via a controlled damage and repair mechanism. DERMO-COSMETICS WITH BIO-ACTIVES There are innovative dermo-cosmetic products containing bio-stimulating ingredients, working more superficial in comparison to in-office treatments and they therefor are potentially an excellent choice as adjunctive care for biological rejuvenation and revitalization for younger looking and acting skin. They are safe to use easy to apply over face, neck and décolletage. Unlike in-office treatments their effects are temporary (fully reversible as regulated), hence they require daily or twice daily application. Bio-stimulating active ingredients in skincare which have shown to particularly stimulate the fibroblast are for example:
VITAMIN C IS NEEDED FOR COLLAGEN SYNTHESES! Our skin needs Vitamin C to produce collagen and is not able to produce it, thus relies on external resources for supply. Therefore I highly recommend to either get enough Vitamin C from your diet or use a high quality topical product pre & post biostimulators. Read more As the biological degeneration takes place in different layers of the skin and it's underlying structures, combining in-office treatments specifically targeting those layers in a series of treatments may provide longer lasting results and give higher patient satisfaction.(13) Safety and outcome rely on the qualification and experience of your cosmetic doctor, dermatologist or plastic surgeon. Take care Special thanks MD FAAD Hassan Galadari Jair Mauricio Cerón Bohórquez M.D. References: 1. American Society Plastic Surgeons. 2020 national plastic surgery statistics; 2020. 2. Wat H, Wu DC, Goldman MP. Noninvasive body contouring: a male perspective. Dermatol Clin. 2018;36(1):49–55. 3. Wang JV, Akintilo L, Geronemus RG. Growth of cosmetic procedures in millennials: a 4.5-year clinical review. J Cosmet Dermatol. 2020;19(12):3210–3212. 4. Evaluation of the biostimulatory effects and the level of neocollagenesis of dermal fillers: a review. Haddad S, Galadari H, Patil A, Goldust M, Al Salam S, Guida S International Journal of Dermatology, 29 Apr 2022 5. J Clin Aesthet Dermatol. 2015 Jan; 8(1): 38–49. Calcium Hydroxylapatite Over a Decade of Clinical Experience Jani Van Loghem, MD, Yana Alexandrovna Yutskovskaya, MD,b and WM. Philip Werschler, MDc 6. Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2022; 15: 997–1019. Collagen Stimulators in Body Applications: A Review Focused on Poly-L-Lactic Acid (PLLA) Marie-Odile Christen Read more 7. Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2020; 13: 31–48. Polycaprolactone: How a Well-Known and Futuristic Polymer Has Become an Innovative Collagen-Stimulator in Esthetics Marie-Odile Christen and Franco Vercesi 8. Oh SH, Lee Y, Seo YJ, Lee JH, Yang JD, Chung HY, Cho BC. The potential effect of botulinum toxin type A on human dermal fibroblasts: an in vitro study. Dermatol Surg. 2012 Oct;38(10):1689-94. 9. El-Domyati M, Attia SK, El-Sawy AE, Moftah NH, Nasif GA, Medhat W, Marwan B. The use of Botulinum toxin-a injection for facial wrinkles: a histological and immunohistochemical evaluation. J Cosmet Dermatol. 2015 Jun;14(2):140-4 10 EADV 2022 Inhibition of extracellular matrix degrading enzymes and bio-stimulation of fibroblasts – A novel approach to mitigate the advanced degenerative process in skin aging Weise J, Vogelsang A, Sperling G, Welge V, Nölter A, Mielke H, Knott A, Harbig S, Stuhr A, Dunckel J, Warnke K, Geloven van A 11. EADV 2021 Multifaceted novel approach to increase skin’s own epidermal and dermal hyaluron content Bussmann T, Warnke K, Krüger A, Möller N, Harbig S, Stuhr A, Dunckel J, Geloven van A, Weise J | Beiersdorf AG, Hamburg, Germany 12. Photochemistry and Photobiology, 2005, 81: 581–587 Novel Aspects of Intrinsic and Extrinsic Aging of Human Skin: Beneficial Effects of Soy Extract Kirstin M. Su¨del et al 13. Combination Therapy in Midfacial Rejuvenation Humphrey et al. Dermatologic Surgery 42:p S83-S88, May 2016. *AMWC 2023 Tapan Patel |
CategoriesAll Acne Ageing Aquatic Wrinkles Armpits Biostimulators Blue Light & HEVIS Cleansing CoQ10 Cosmetic Intolerance Syndrome Deodorant Dermaplaning Diabetes Dry Skin Evidence Based Skin Care Exfoliation Exosomes Eyes Face Or Feet? Facial Oils Fibroblast Fingertip Units Gendered Ageism Glycation Gua Sha Hair Removal Healthy Skin Heat Shock Proteins Hormesis Humidity Hyaluron Hyaluronidase Hypo-allergenic Indulging Jade Roller Licochalcone A Luxury Skin Care Lymphatic Vessel Ageing Malar Oedema Menopause Mitochondrial Dysfunction Mood Boosting Skin Care Neurocosmetics Ox Inflammageing PH Balance Skin Photo Biomodulation Polynucleotides Psoriasis Regenerative Treatments Review Safety Scarring Sensitive Skin Skin Care Regimen Skin Flooding Skin Hydration Skin Senescence Skip-Care Sleep Slugging Sunscreen Tanning Under Eye Bags Vitamin C Well Ageing Skin Care Wound Healing Wrinkles
Archives
April 2024
|


 RSS Feed
RSS Feed
